I know people are going to start getting sick of me... I ask a lot of questions and everyone must be thinking 'buy a Mac and be done with it' but there are things I keep thinking of that may cause me a problem when I switch over - so need to be rectified before I start playing around with the new Mac =).
I am currently composing a Web Site using Dreamweaver (no real issue there because Dreamweaver is also available on the Mac). I am a newbie to Dreamweaver, and am learning as I go along. I am just setting up IIS on my laptop as I have some scripts I would like to test without having to use an online web server.
Can someone tell me what the Mac equivilent of IIS would be so that I will be able to carry on creating my site even after I move to my MBP?
Thanks!!
Sony Vaio, Windows XP Pro, 2.8Ghz Intel P4, 512MB Memory
Posted on

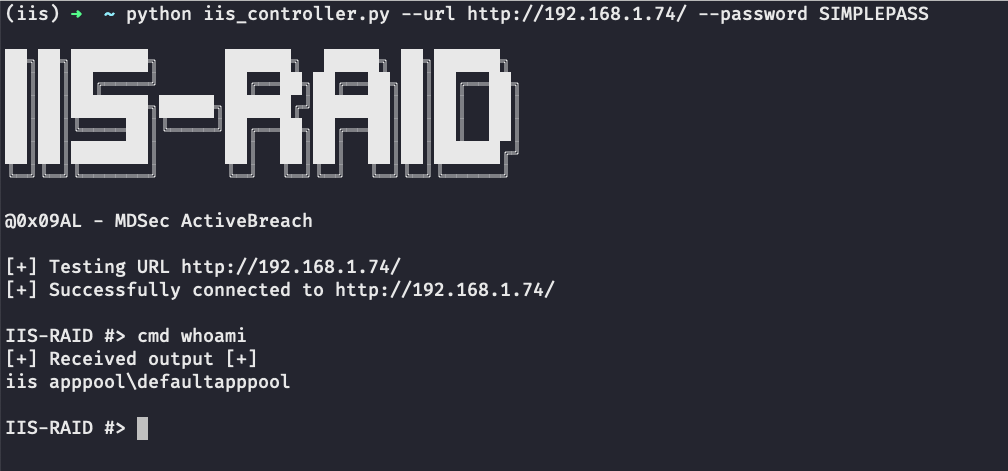
Nginx engine x is a HTTP and reverse proxy server, as well as a mail proxy server. IIS doesn't run on Mac, so I guess you should try Apache, and then install module 'modmono'. Or if that gets too hairy, just use the standalone mono. The web.config file that IIS uses to configure the website, including the required redirect rules and file content types. The app's static asset folder. Host as an IIS sub-app. If a standalone app is hosted as an IIS sub-app, perform either of the following: Disable the inherited ASP.NET Core Module handler. Visual Studio for Mac provides integrated support for developing and deploying your microservices using Docker containers. Containerize your.NET Core app by adding support right from the Solution Pad. Launch a professional environment tailored to the Mac, free for most non-enterprise users. Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.0 (Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008) introduced application pool identity, a new isolation mechanism that helps provide increased security for servers that run ASP.NET applications. However, sites that are running under the application pool identity do not have access to the HKCU registry.
-->by Keith Newman and Robert McMurray
This document shows you how to use common request-filter settings to improve the security of your IIS 8 web server.
Request filters restrict the types of HTTP requests that IIS 8 processes. By blocking specific HTTP requests, request filters help prevent potentially harmful requests from reaching the server. The request filter module scans incoming requests and rejects requests that are unwanted based upon the rules that you set up.
By default, IIS rejects requests to browse critical code segments. It also rejects requests for some file name extensions.
You can configure a request filter at the server-wide level and then override the configuration at a website level.
Prerequisites
To get the most from this tutorial, you must have access to a computer that is running one of the following operating systems:
- Windows Server® 2012
- Windows® 8
General Request Filter Settings
The general settings include such settings as the following:
- Whether to allow access to a file with an extension that is not listed for request filter.
- Whether to allow requests that use HTTP verbs that are not listed.
- Whether to allow requests that contain high-bit characters (non-ASCII).
- Whether to allow requests that are double encoded.
- Maximum length of the content requested.
- Maximum length of the URL.
- Maximum size of a query string.
To configure general request-filter options by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- In the Actions pane, click Edit Feature Settings.
- In the Edit Request Filtering Settings dialog, edit the settings as desired, and then click OK.
To configure general request-filter options by using the command line
Configure high-bit characters
To configure high-bit characters, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /allowhighbitcharacters:true|false
For example, to allow high-bit characters, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /allowhighbitcharacters:true
Configure double escaping
To configure double escaping, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /allowdoubleescaping:true|false
For example, to enable double escaping, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /allowdoubleescaping:true
Configure the maximum allowed content length
To configure a value for the maximum allowed length of content, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxallowedcontentlength:unit
The variable requestlimits.maxallowedcontentlength:unit specifies the maximum length of content.
For example, to specify 30000000 as the maximum length of content, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxallowedcontentlength:30000000
Configure the maximum allowed URL length
To configure a value for the maximum allowed length of an incoming URL, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxurl:unit
The variable requestlimits.maxurl:unit specifies the maximum length of an incoming URL.
For example, to specify 4096 as the maximum incoming URL length, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxurl:4096
Configure the maximum allowed query string length
To configure a value for the maximum allowed length of an incoming query string, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxquerystring:unit
The variable requestlimits.maxquertystring:unit specifies the maximum length of an incoming query string.
For example, to specify 2048 as the maximum incoming query string, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxquerystring:2048
Configure the maximum size for an HTTP header
To configure a size limit for a specific HTTP header, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+requestlimits.headerLimits.[header='string',sizelimit='unit']
The variable header=string specifies the header this restriction applies to. The variable sizelimit=unit specifies the maximum size of this header.
For example, to specify a maximum size of 2048 for headers that include a value of contoso.com, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+requestlimits.headerLimits.[header='contoso.com',sizelimit='2048']
File Name Extensions
For each file name extension you add, you can indicate whether to allow or reject requests for that type of file.
To configure file name extensions by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the File Name Extensions tab.
- In the Actions pane, click either Allow File Name Extension or Deny File Name Extension.
- Type the file name extension in the box, and then click OK.
To configure file name extensions by using the command line
Configure unlisted file name extensions
To configure how IIS deals with unlisted file name extensions, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /fileExtensions.allowunlisted:true|false
For example, to deny unlisted file name extensions, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /fileExtensions.allowunlisted:false
Configure for WebDAV requests
To configure whether file name extensions apply to WebDAV requests, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /fileExtensions.applyToWebDAV:true|false
For example, to configure IIS so that file name extensions do not apply to WebDAV requests, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /fileExtensions.applyToWebDAV:false
Add or remove a file name extension
To add a file name extension, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+fileExtensions.[fileextension='string',allowed='true | false']
The variable fileextension=string is the file name extension you want to allow or deny.
For example, to add an allow rule for the file name extension .xxx, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+fileExtensions.[fileextension='.xxx',allowed='true']
To remove a rule for the file name extension .xxx, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /-fileExtensions.[fileextension='.xxx']
Filtering Rules
IIS 8 permits you to define custom filter rules that apply to incoming requests. Using this feature, you can define filters that can do the following:
- Scan the request URL.
- Scan for query strings contained in the URL.
- Scan for specific header fields.
- Define what file name extensions the filter applies to.
- Define strings you want to deny.
To configure a filtering rule by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the Rules tab.
- In the Actions pane, double-click Add Filtering Rule.
- In the Name box, type a name for the filtering rule.
- If you want the URL scanned, select the Scan Url check box.
- If you want the query string scanned, select the Scan query string check box.
- Under Scan Headers, type one or more headers to scan for.
- Under Applies To, type one or more file name extensions that the rule applies to.
- Under the Deny Strings, type one or more strings you want to deny.
- Click OK.
Hidden Segments
This feature allows you to reject requests that contain a URL segment (for example, a folder name).
To configure hidden segments by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the Hidden Segments tab.
- In the Actions pane, click Add Hidden Segment.
- Type the URL segment in the box, and then click OK.
To configure hidden segments by using the command line
Configure for WebDAV requests
To configure whether hidden segments apply to WebDAV requests, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /hiddensegments.applyToWebDAV:true|false
For example, to configure IIS so that hidden segments do not apply to WebDAV requests, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /hiddensegments.applyToWebDAV:false
Add a hidden segment
To configure a hidden segment, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+hiddensegments.[segment='string']
The variable segment=string specifies a URL segment that is hidden.
For example, to specify that /bin is a hidden segment, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+hiddensegments.[segment='/bin']
URL Filtering
You can configure IIS to accept a specified URL. In addition, you can configure it to deny a specified URL sequence.
To configure URL filtering by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the URL tab.
- In the Actions pane, select either Allow URL or Deny Sequence.
- Type the URL or the URL sequence in the box, and click OK.
To configure URL filtering by using the command line
To deny a URL sequence, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+denyurlsequences.[sequence='string']
The variable sequence=string specifies a sequence of characters in a URL that IIS is never allowed to parse.
For example, to specify that IIS never parse URLs that contain two periods, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+denyurlsequences.[sequence='..']
HTTP Verbs
You can define a list of verbs that IIS 8 accepts as part of a request. When IIS rejects a request based on this feature, the error code logged is 404.6.
To configure unlisted HTTP verbs by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the HTTP Verbs tab.
- In the Actions pane, click either Allow Verb or Deny Verb.
- Enter the verb in the box, and then click OK.
To configure unlisted HTTP verbs by using the command line
Configure unlisted HTTP verbs
To configure how IIS deals with unlisted verbs, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /verbs.allowunlisted:true|false
For example, to deny unlisted verbs, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /verbs.allowunlisted:false
Configure for WebDAV requests
To configure whether verb filtering applies to WebDAV requests, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /verbs.applyToWebDAV:true|false

For example, to configure IIS so that verb filtering does not apply to WebDAV requests, type the following at the command prompt and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /verbs.applyToWebDAV:false
Add an HTTP verb
To configure a verb to filter, use the following syntax:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+verbs.[verb='string',allowed='true|false']
The variable verb=string specifies the verb this restriction applies to.
For example, to specify GET is allowed, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /+verbs.[verb='GET',allowed='true']
Header Size Limits
You can limit the size of HTTP request headers to improve performance and security. Headers are name/value pairs that define the operating parameters of an HTTP transaction.
To configure header size limits by using the UI
- Open IIS Manager and select the level for which you want to configure request filter.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the Headers tab, and click Add Header.
- In the Header box, type the header field name.
- In the Size Limit box, type a positive integer that represents the header size limit in bytes.
- Click OK.
Query Strings
You can configure IIS 8 to allow or deny specific query strings contained in the requested URL. For example, if a denied query string is found in a request URL, the request is denied.
To configure query strings by using the UI
Vmware Mac Os X Image
- Open IIS Manager and select the level where you want to configure request filtering.
- In Features View, double-click Request Filtering.
- Select the Query Strings tab, and click either Allow Query String or Deny Query String.
- In the Query string box, type the query string.
- Click OK.
Mac Os Download
Request Filter Logging
You can use IIS logging to evaluate and optimize your request filter configuration.
The following table shows the request filter error codes that you see in the log:
| Error Description | Status Code |
|---|---|
| Request Filtering: URL Sequence denied | 404.5 |
| Request Filtering: Verb denied | 404.6 |
| Request Filtering: File name extension denied | 404.7 |
| Request Filtering: Denied by hidden segment | 404.8 |
| Request Filtering: Denied because URL doubled escaping | 404.11 |
| Request Filtering: Denied because of high bit characters | 404.12 |
| Request Filtering: Denied because URL too long | 404.14 |
| Request Filtering: Denied because query string too long | 404.15 |
| Request Filtering: Denied because content length too large | 413.1 |
| Request Filtering: Denied because request header is too long. | 431 |
Mac Os X Installer Download
See Also
